Automated Failover to GKE with Terraform, CI/CD, and ArgoCD
I created a fully automated disaster recovery solution for my Kubernetes homelab using CI/CD, Terraform, Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE), and ArgoCD. It adds a safety net in case I lose power, WiFi, or need to perform physical maintenance on my Raspberry Pis. I host live demos on my cluster so this solution allows me to maximize uptime.
Table of Contents
- Prerequisites
- Architecture
- Cost Breakdown
- HTTP Health Check Pipeline
- GKE Deployment Pipeline
- Terraform Code for Cluster (Infra)
- Terraform Code for Workloads
- Terraform Destroy Pipeline
- Final Outcome
Prerequisites
- Terraform
- GitHub Actions
- GCP service account (needed for Terraform assign a k8s ClusterRole to)
- ArgoCD app
Architecture
GitHub repo: https://github.com/dstanecki/zillow-housing-forecast
I run a k8s cluster on my homelab consisting of 3 nodes. My app has readiness and liveliness probes for smart traffic redirection on the pod level. However, I wanted to have a solution for cluster-wide failure. I’ve yet to experience unplanned total failure, but sometimes I have to unplug my server rack for maintenance and I like having the option to keep my live demos running while I do so.
A health check job pings an HTTP endpoint in my cluster’s app every 5 minutes and triggers the GKE pipeline after 3 consecutive failures. The GKE pipeline deploys the app to cloud in a zero-touch fashion and redirects the DNS record.
I opted to divide my Terraform code into two main.tf files - one for the infrastructure and required packages (e.g. infra helm charts) and one for the workloads (ArgoCD apps, etc.). Since I would be seldom changing the infrastructure, this structure let me separate workloads from infra more coherently. Also, it ensured that the cluster was ready before the workloads tried to access its API. In my early stages of testing I needed to use a wait condition, but this method let me do away with that.
I chose GKE because it has a good free tier and seems to have more features than AWS and Azure’s offerings. I also want to familiarize myself with GCP in general because the bulk of my infrastructure experience has been with AWS. I’m using Standard GKE instead of Autopilot since I want to keep things as consistent with my on-prem cluster as possible. The primary factor being that Autopilot has its own Google-managed ingress configured and I want to keep using Traefik.
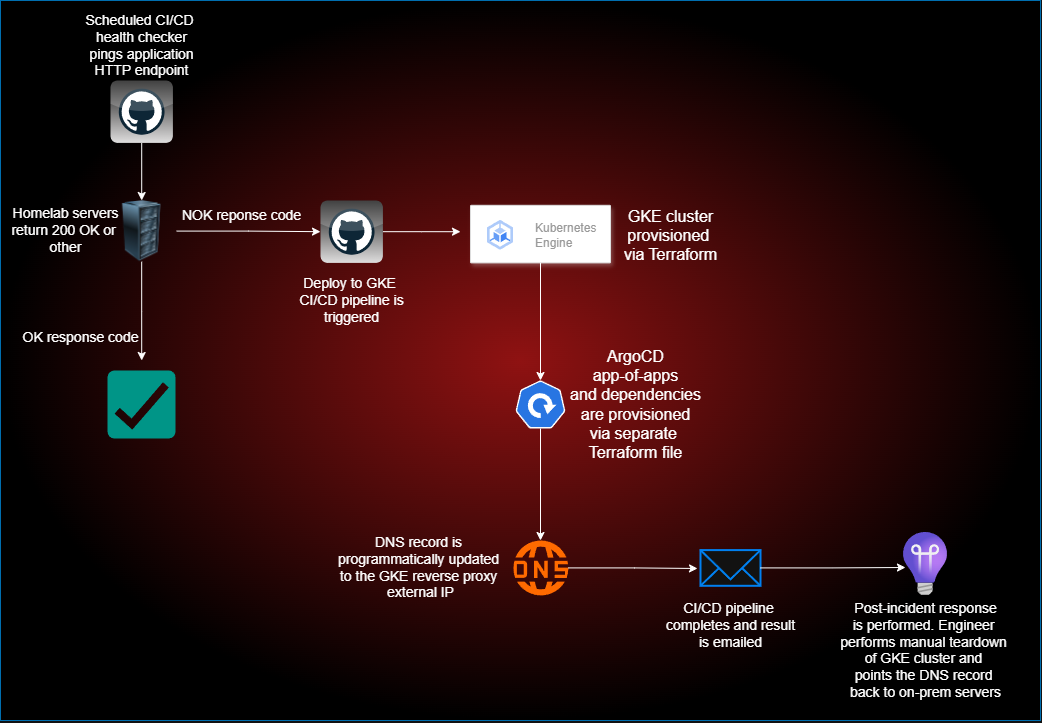 |
|---|
| Figure: Disaster recovery workflow from homelab to GKE |
Cost Breakdown
I haven’t been impressed with GCP’s resource availability compared to AWS, having received numerous errors about it thus far. Because of this, I’m going to avoid using Spot/preemptible instances.
GKE offers a free tier for your first cluster, meaning you still have to pay for the VMs but you do not pay a cluster management fee ($0.10/hr). Knowing this, I’m opting to stick with a single zone cluster using two nodes. If I were running any production critical workloads, I would use a regionally available cluster shown in Option 2 in the table:
| Cluster Type | Description | Nodes | Est. VM Cost (Total) | GKE Cluster Fee | Monthly Cost | Daily Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zonal | 2× e2-standard-2 nodes in single zone |
2 | ~$73 × 2 = $146 | Free (1st zonal cluster) | ~$146 | ~$4.87 |
| Regional | 3× e2-standard-2 nodes across 3 zones |
3 | ~$73 × 3 = $219 | ~$73 (regional fee) | ~$292 | ~$9.73 |
Currently, my workloads need at least 16GB of RAM which I what I have in my home lab. I’m using autoscaling with a minimum of 2 e2-standard-2 VMs to match that figure.
HTTP Health Check Pipeline
I opted to use GitHub Actions for CI/CD since I can use their worker agents for free and it can run up to every 5 minutes. In the real world, the worker cron schedule is delayed more often than not, so I would recommend using a dedicated agent for sensitive scenarios.
The health checks are done with curling my /ready endpoint defined in my Python app and consecutive failures are cached in a hidden .cache directory. In the last step, I trigger the deployment pipeline using a POST call to github API if the fail count reaches 3.
name: Ping Endpoint
on:
schedule:
- cron: "*/5 * * * *" # every 5 minutes (quickest frequency allowed)
workflow_dispatch: # allows manual trigger
jobs:
ping-endpoint:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Ping endpoint
id: ping
run: |
response=$(curl -s -o /dev/null -w "%{http_code}" https://zhf.danielstanecki.com/ready)
echo "HTTP status: $response"
echo "response_code=$response" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
- name: Check status code and set failure flag
id: check
run: |
if [ "${{ steps.ping.outputs.response_code }}" != "200" ]; then
echo "status=fail" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
else
echo "status=ok" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
fi
- name: Cache failure count
uses: actions/cache@v3
with:
path: .cache
key: ping-status
- name: Load and update failure count
id: failure-count
run: |
mkdir -p .cache
file=".cache/failure_count.txt"
count=0
[ -f "$file" ] && count=$(cat "$file")
if [ "${{ steps.check.outputs.status }}" == "fail" ]; then
count=$((count+1))
else
count=0
fi
echo "$count" > "$file"
echo "fail_count=$count" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
echo "Current failure count: $count"
- name: Trigger Deploy to GKE
if: ${{ steps.failure-count.outputs.fail_count >= 3 }}
env:
GH_PAT: ${{ secrets.GH_PAT }}
run: |
curl -X POST https://api.github.com/repos/${{ github.repository }}/dispatches \
-H "Authorization: token $GH_PAT" \
-H "Accept: application/vnd.github.v3+json" \
-d '{"event_type": "trigger-fallback"}'
GKE Deployment Pipeline
The pipeline code has 4 main components.
- Checkout repo and set up prerequisites (GCP, Terraform)
- Run infrastructure Terraform plan
- Run workloads Terraform plan
- Modify DNS record
name: Terraform GKE Deployment
on:
repository_dispatch:
types: [trigger-fallback]
workflow_dispatch:
env:
TF_VAR_project_id: ${{ secrets.GCP_PROJECT_ID }}
TF_VAR_db_password: ${{ secrets.DB_PASSWORD }}
TF_VAR_azure_ai_openapi_key: ${{ secrets.AZURE_AI_OPENAPI_KEY }}
TF_VAR_recaptcha_secret_key_prod: ${{ secrets.RECAPTCHA_SECRET_KEY_PROD }}
TF_VAR_recaptcha_secret_key_dev: ${{ secrets.RECAPTCHA_SECRET_KEY_DEV }}
TF_VAR_redis_password: ${{ secrets.REDIS_PASSWORD }}
TF_VAR_cloudflare_api_token_secret: ${{ secrets.CLOUDFLARE_API_TOKEN }}
jobs:
terraform:
name: Deploy with Terraform
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout repository
uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Set up Terraform
uses: hashicorp/setup-terraform@v3
with:
terraform_version: 1.12.2
- name: Authenticate with Google Cloud
uses: google-github-actions/auth@v2
with:
credentials_json: '${{ secrets.GOOGLE_CREDENTIALS }}'
- name: Set up Google Cloud SDK
uses: google-github-actions/setup-gcloud@v2
- name: Cluster Terraform Init
working-directory: terraform/cluster
run: terraform init
- name: Cluster Terraform Plan
working-directory: terraform/cluster
run: terraform plan
- name: Cluster Terraform Apply
working-directory: terraform/cluster
run: terraform apply -auto-approve
- name: Get Traefik IP
id: traefik-ip
working-directory: terraform/cluster
run: |
ip=$(terraform output -raw traefik_load_balancer_ip)
echo "traefik_ip=$ip" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
# APPLY WORKLOADS e.g. ArgoCD apps
- name: Workloads Terraform Init
working-directory: terraform/workloads
run: terraform init
- name: Workloads Terraform Plan
working-directory: terraform/workloads
run: terraform plan
- name: Workloads Terraform Apply
working-directory: terraform/workloads
run: terraform apply -auto-approve
- name: Update DNS record
run: |
ip="${{ steps.traefik-ip.outputs.traefik_ip }}"
curl -X PATCH "https://api.cloudflare.com/client/v4/zones/$ZONE_ID/dns_records/$DNS_RECORD_ID" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $CLOUDFLARE_API_TOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d "{\"name\":\"zhf.danielstanecki.com\",\"type\":\"A\",\"comment\":\"Domain verification record\",\"content\":\"$ip\",\"proxied\":true}"
env:
CLOUDFLARE_API_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.CLOUDFLARE_API_TOKEN }}
ZONE_ID: ${{ secrets.CLOUDFLARE_ZONE_ID }}
DNS_RECORD_ID: ${{ secrets.DNS_RECORD_ID }}
Cluster (Infra) Terraform
Here I deploy the providers, GKE cluster, namespaces, and infra-related Helm charts. The values for argoCD Helm and cert-manager Helm must specify .crds.keep=false to ensure a smooth Terraform destroy.
provider "google" {
project = var.project_id
region = var.region
}
provider "helm" {
kubernetes = {
host = "https://${google_container_cluster.zhf_cluster.endpoint}"
token = data.google_client_config.default.access_token
cluster_ca_certificate = base64decode(google_container_cluster.zhf_cluster.master_auth[0].cluster_ca_certificate)
}
}
provider "kubernetes" {
host = "https://${google_container_cluster.zhf_cluster.endpoint}"
token = data.google_client_config.default.access_token
cluster_ca_certificate = base64decode(google_container_cluster.zhf_cluster.master_auth[0].cluster_ca_certificate)
}
data "google_client_config" "default" {}
resource "google_compute_network" "zhf_network" {
name = "zhf-network"
auto_create_subnetworks = false
enable_ula_internal_ipv6 = true
}
resource "google_compute_subnetwork" "zhf_subnetwork" {
name = "zhf-subnetwork"
ip_cidr_range = "10.0.0.0/16"
region = var.region
stack_type = "IPV4_IPV6"
ipv6_access_type = "INTERNAL" # Change to "EXTERNAL" if creating an external loadbalancer
network = google_compute_network.zhf_network.id
secondary_ip_range {
range_name = "services-range"
ip_cidr_range = "192.168.16.0/24"
}
secondary_ip_range {
range_name = "pod-ranges"
ip_cidr_range = "192.168.0.0/20"
}
}
resource "google_container_cluster" "zhf_cluster" {
name = var.cluster_name
location = var.zone # SINGLE ZONE DEPLOYMENT
remove_default_node_pool = true
initial_node_count = 2
enable_l4_ilb_subsetting = true
network = google_compute_network.zhf_network.id
subnetwork = google_compute_subnetwork.zhf_subnetwork.id
ip_allocation_policy {
# stack_type = "IPV4_IPV6"
services_secondary_range_name = google_compute_subnetwork.zhf_subnetwork.secondary_ip_range[0].range_name
cluster_secondary_range_name = google_compute_subnetwork.zhf_subnetwork.secondary_ip_range[1].range_name
}
deletion_protection = false
timeouts {
create = "20m"
update = "20m"
delete = "15m"
}
}
resource "google_container_node_pool" "zhf_node_pool" {
name = "zhf-node-pool"
cluster = google_container_cluster.zhf_cluster.name
location = var.zone
autoscaling {
min_node_count = 2
max_node_count = 3
}
node_config {
machine_type = "e2-standard-2"
oauth_scopes = [
"https://www.googleapis.com/auth/cloud-platform",
]
}
management {
auto_repair = true
auto_upgrade = true
}
upgrade_settings {
max_surge = 1
max_unavailable = 0
}
}
# Install ArgoCD
resource "helm_release" "argocd" {
name = "argocd"
namespace = "argocd"
repository = "https://argoproj.github.io/argo-helm"
chart = "argo-cd"
version = "8.1.3" # check latest: https://artifacthub.io/packages/helm/argo/argo-cd
create_namespace = true
values = [file("../../argo/apps/argocd/values.yaml")]
}
resource "helm_release" "cert_manager" {
name = "cert-manager"
namespace = "cert-manager"
repository = "https://charts.jetstack.io"
chart = "cert-manager"
version = "v1.18.0"
create_namespace = true
values = [file("../../argo/apps/cert-manager/values.yaml")]
}
resource "helm_release" "kube_prometheus_stack" {
name = "kube-prometheus-stack"
namespace = "monitoring"
repository = "https://prometheus-community.github.io/helm-charts"
chart = "kube-prometheus-stack"
version = "75.11.0"
create_namespace = true
}
resource "helm_release" "traefik" {
name = "traefik"
namespace = "kube-system"
repository = "https://helm.traefik.io/traefik"
chart = "traefik"
version = "36.3.0"
create_namespace = true
}
data "kubernetes_service" "traefik" {
metadata {
name = "traefik"
namespace = "kube-system"
}
depends_on = [helm_release.traefik]
}
resource "kubernetes_namespace" "dev" {
metadata {
name = "dev"
}
}
resource "kubernetes_namespace" "prod" {
metadata {
name = "prod"
}
}
Workloads Terraform
Sets up GCP service account privileges for k8s, which is necessary even if it has admin permissions at the GCP level. Set up secrets from ENV vars. Deploy ArgoCD app-of-apps (also manages infra apps that were installed by the cluster terraform code).
provider "google" {
project = var.project_id
region = var.region
}
data "google_client_config" "default" {}
data "terraform_remote_state" "cluster" {
backend = "gcs"
config = {
bucket = "zhf-tfstate-bucket"
prefix = "terraform/cluster"
}
}
locals {
k8s_connection = {
host = "https://${data.terraform_remote_state.cluster.outputs.cluster_endpoint}"
token = data.google_client_config.default.access_token
cluster_ca_certificate = base64decode(data.terraform_remote_state.cluster.outputs.ca_certificate)
}
}
provider "kubernetes" {
host = local.k8s_connection.host
token = local.k8s_connection.token
cluster_ca_certificate = local.k8s_connection.cluster_ca_certificate
}
provider "helm" {
kubernetes = local.k8s_connection
}
# Give GCP service account k8s privilege
resource "kubernetes_cluster_role_binding" "terraform_cluster_admin" {
metadata {
name = "terraform-cluster-admin"
}
role_ref {
api_group = "rbac.authorization.k8s.io"
kind = "ClusterRole"
name = "cluster-admin"
}
subject {
kind = "User"
name = var.terraform_service_account_email
api_group = "rbac.authorization.k8s.io"
}
}
# SECRETS
resource "kubernetes_secret" "db_password_dev" {
metadata {
name = "db-password"
namespace = "dev"
}
data = {
DB_PASSWORD = var.db_password
}
type = "Opaque"
}
resource "kubernetes_secret" "db_password_prod" {
metadata {
name = "db-password"
namespace = "prod"
}
data = {
DB_PASSWORD = var.db_password
}
type = "Opaque"
} # ...
# Install app of apps
resource "kubernetes_manifest" "app_of_apps" {
manifest = {
apiVersion = "argoproj.io/v1alpha1"
kind = "Application"
metadata = {
name = "app-of-apps"
namespace = "argocd"
}
spec = {
project = "default"
source = {
repoURL = "https://github.com/dstanecki/zillow-housing-forecast.git"
targetRevision = "HEAD"
path = "argo/apps"
directory = {
recurse = true
}
}
destination = {
server = "https://kubernetes.default.svc"
namespace = "argocd"
}
syncPolicy = {
automated = {
prune = true
selfHeal = true
}
}
}
}
}
Terraform Destroy Pipeline
Deletes all CRDs, certain finalizers that prevent deletion, terraform state components that prevent deletion, and sets the DNS record back to homelab cluster.
name: Terraform Destroy
on:
workflow_dispatch:
env:
TF_VAR_project_id: ${{ secrets.GCP_PROJECT_ID }}
TF_VAR_db_password: ${{ secrets.DB_PASSWORD }}
TF_VAR_azure_ai_openapi_key: ${{ secrets.AZURE_AI_OPENAPI_KEY }}
TF_VAR_recaptcha_secret_key_prod: ${{ secrets.RECAPTCHA_SECRET_KEY_PROD }}
TF_VAR_recaptcha_secret_key_dev: ${{ secrets.RECAPTCHA_SECRET_KEY_DEV }}
TF_VAR_redis_password: ${{ secrets.REDIS_PASSWORD }}
TF_VAR_cloudflare_api_token_secret: ${{ secrets.CLOUDFLARE_API_TOKEN }}
USE_GKE_GCLOUD_AUTH_PLUGIN: "True"
jobs:
terraform:
name: Destroy all
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout repository
uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Set up Terraform
uses: hashicorp/setup-terraform@v3
with:
terraform_version: 1.12.2
- name: Authenticate with Google Cloud
uses: google-github-actions/auth@v2
with:
credentials_json: '${{ secrets.GOOGLE_CREDENTIALS }}'
- name: Set up Google Cloud SDK
uses: google-github-actions/setup-gcloud@v2
# Destroy workloads
- name: Terraform Init (workloads)
working-directory: terraform/workloads
run: terraform init
- name: Terraform Destroy Workloads
working-directory: terraform/workloads
run: terraform destroy -auto-approve
# Get region from terraform output
- name: Terraform Init (cluster)
working-directory: terraform/cluster
run: terraform init
- name: Extract zone from Terraform
working-directory: terraform/cluster
id: tf_outputs
run: |
ZONE=$(terraform output -raw zone)
echo "ZONE=$ZONE" >> $GITHUB_ENV
- name: Install gke-gcloud-auth-plugin
run: |
gcloud components install gke-gcloud-auth-plugin --quiet
# Configure kubectl with dynamic zone
- name: Configure kubectl
run: |
gcloud container clusters get-credentials zhf-cluster \
--zone "$ZONE" \
--project "$TF_VAR_project_id"
# Force delete stuck namespaces (finalizers)
- name: Force delete stuck namespaces
run: |
for ns in dev prod; do
kubectl get namespace $ns -o json 2>/dev/null | \
jq 'del(.spec.finalizers)' | \
kubectl replace --raw "/api/v1/namespaces/$ns/finalize" -f - || true
done
# Clean up CRDs and Terraform state
- name: Clean up CRDs and namespace state
working-directory: terraform/cluster
run: |
kubectl delete crd --all --ignore-not-found || true
terraform state rm 'helm_release.cert_manager' || true
terraform state rm 'helm_release.kube_prometheus_stack' || true
terraform state rm 'helm_release.traefik' || true
terraform state rm 'kubernetes_namespace.dev' || true
terraform state rm 'kubernetes_namespace.prod' || true
- name: Terraform Destroy Cluster
working-directory: terraform/cluster
run: terraform destroy -auto-approve
- name: Update DNS record
run: |
curl -X PATCH "https://api.cloudflare.com/client/v4/zones/$ZONE_ID/dns_records/$DNS_RECORD_ID" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $CLOUDFLARE_API_TOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"name": "zhf.danielstanecki.com",
"type": "CNAME",
"comment": "Domain verification record",
"content": "'"$ONPREM_DNS_RECORD"'",
"proxied": true
}'
env:
ONPREM_DNS_RECORD: ${{ secrets.ONPREM_DNS_RECORD }}
CLOUDFLARE_API_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.CLOUDFLARE_API_TOKEN }}
ZONE_ID: ${{ secrets.CLOUDFLARE_ZONE_ID }}
DNS_RECORD_ID: ${{ secrets.DNS_RECORD_ID }}
Final Outcome
The entire pipeline produces a failover solution that completes in 35 minutes; 15 minutes for health check failures and 20 minutes for actual deployment. I don’t think it’s ideal being limited to health checks every 5 minutes (and often delayed) and in the future I might consider switching to a self-hosted runner instead.
For planned maintenance, I can now do a zero-downtime failover by just running the pipeline manually.